Neofetch – Script bash pour afficher vos informations systèmes
La commande neofetch est écrite dans un shell bash. L’objectif principal de neofetch est d’être utilisé dans les captures d’écran pour afficher aux autres utilisateurs le système d’exploitation ou la distribution Linux que vous utilisez, y compris le thème, les icônes, la configuration matérielle, etc…
Cette commande affiche des informations sur votre système à côté d’une image, le logo de votre système d’exploitation et d’autres informations. Les informations par défaut sont affichées à côté du logo de votre système d’exploitation. Vous pouvez en outre configurer Neofetch pour utiliser à la place une image, un fichier ASCII personnalisé, votre fond d’écran ou rien du tout. Voyons comment installer et utiliser la dernière version de neofetch sur un système Linux ou de type Unix pour obtenir des informations sur le système.
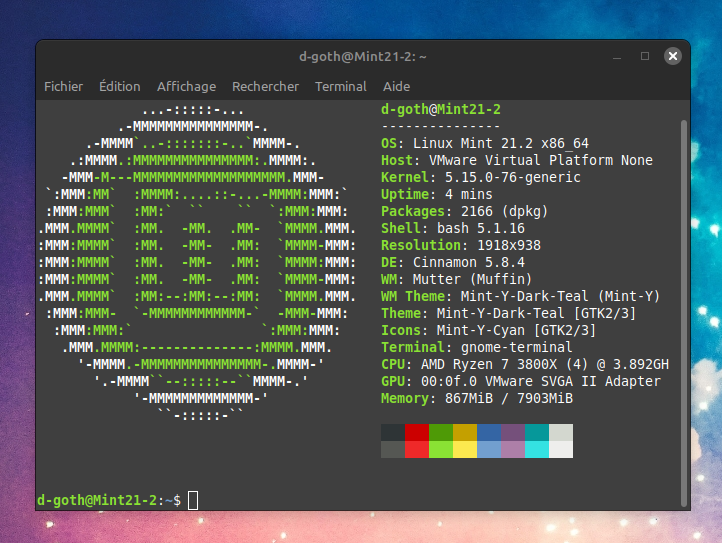
*Capture faite sur une VM pour illustrer le fait, que Neofetch soit pré-installé sur les distributions sur base d’Ubuntu*
Naturellement, vous avez besoin que le shell bash soit installé sur votre système. Instructions à partir de la page d’accueil du projet :
Neofetch est un outil d’information système en ligne de commande écrit en bash 3.2+. Neofetch affiche des informations sur votre système d’exploitation, vos logiciels et votre matériel de manière esthétique et visuellement agréable. L’objectif général de Neofetch est d’être utilisé dans les captures d’écran de votre système. Neofetch affiche les informations que les autres personnes veulent voir. Il existe d’autres outils disponibles pour les statistiques/diagnostics appropriés du système. Neofetch prend en charge près de 150 systèmes d’exploitation différents. De Linux à Windows, jusqu’aux systèmes d’exploitation plus obscurs comme Minix, AIX et Haiku.
Comment installer neofetch
Sur un système de type Linux ou Unix
Tapez la commande wget suivante pour récupérer la dernière archive tar :
wget https://github.com/dylanaraps/neofetch/archive/master.zip
Décompressez le fichier nommé master.zip à l’aide de la commande unzip :
unzip master.zip
$ cd neofetch-master
$ sudo make install
Sur Debian (et beaucoup d’autres ; exemple : Ubuntu & ces déclinaisons (si non-préinstallé)) :
sudo apt-get install neofetch
Sur Fedora :
sudo dnf install neofetch
Sur macOS (Homebrew pré-requis):
export HOMEBREW_NO_INSTALL_FROM_API=1
/bin/bash -c « $(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh) »
brew install neofetch
Comment utiliser la commande neofetch ?
Ouvrez l’application Terminal et saisissez la commande :
neofetch
Et observer le résultat. Vous avez sur votre terminal, le logo de votre OS en ASCII, et la majorité des information systèmes, de votre thème, kernel, ect…
Plus d’informations et d’options pour neofetch ?
Ouvrez votre terminal :
neofetch –help
$ neofetch –help | more
Et voici ce que vous obtenez :
Usage: neofetch --option "value" --option "value"
Neofetch is a CLI system information tool written in BASH. Neofetch
displays information about your system next to an image, your OS logo,
or any ASCII file of your choice.
NOTE: Every launch flag has a config option.
Options:
INFO:
--disable infoname Allows you to disable an info line from appearing
in the output. 'infoname' is the function name from the
'print_info()' function inside the config file.
For example: 'info "Memory" memory' would be '--disable memory'
NOTE: You can supply multiple args. eg. 'neofetch --disable cpu gpu'
--package_managers on/off Hide/Show Package Manager names . (tiny, on, off)
--os_arch on/off Hide/Show OS architecture.
--speed_type type Change the type of cpu speed to display.
Possible values: current, min, max, bios,
scaling_current, scaling_min, scaling_max
NOTE: This only supports Linux with cpufreq.
--speed_shorthand on/off Whether or not to show decimals in CPU speed.
NOTE: This flag is not supported in systems with CPU speed less than
1 GHz.
--cpu_brand on/off Enable/Disable CPU brand in output.
--cpu_cores type Whether or not to display the number of CPU cores
Possible values: logical, physical, off
NOTE: 'physical' doesn't work on BSD.
--cpu_speed on/off Hide/Show cpu speed.
--cpu_temp C/F/off Hide/Show cpu temperature.
NOTE: This only works on Linux and BSD.
NOTE: For FreeBSD and NetBSD-based systems, you need to enable
coretemp kernel module. This only supports newer Intel processors.
--distro_shorthand on/off Shorten the output of distro (tiny, on, off)
NOTE: This option won't work in Windows (Cygwin)
--kernel_shorthand on/off Shorten the output of kernel
NOTE: This option won't work in BSDs (except PacBSD and PC-BSD)
--uptime_shorthand on/off Shorten the output of uptime (tiny, on, off)
--refresh_rate on/off Whether to display the refresh rate of each monitor
Unsupported on Windows
--gpu_brand on/off Enable/Disable GPU brand in output. (AMD/NVIDIA/Intel)
--gpu_type type Which GPU to display. (all, dedicated, integrated)
NOTE: This only supports Linux.
--gtk_shorthand on/off Shorten output of gtk theme/icons
--gtk2 on/off Enable/Disable gtk2 theme/font/icons output
--gtk3 on/off Enable/Disable gtk3 theme/font/icons output
--shell_path on/off Enable/Disable showing $SHELL path
--shell_version on/off Enable/Disable showing $SHELL version
--disk_show value Which disks to display.
Possible values: '/', '/dev/sdXX', '/path/to/mount point'
NOTE: Multiple values can be given. (--disk_show '/' '/dev/sdc1')
--disk_subtitle type What information to append to the Disk subtitle.
Takes: name, mount, dir
'name' shows the disk's name (sda1, sda2, etc)
'mount' shows the disk's mount point (/, /mnt/Local Disk, etc)
'dir' shows the basename of the disks's path. (/, Local Disk, etc)
--ip_host url URL to query for public IP
--song_format format Print the song data in a specific format (see config file).
--song_shorthand on/off Print the Artist/Album/Title on separate lines.
--music_player player-name Manually specify a player to use.
Available values are listed in the config file
TEXT FORMATTING:
--colors x x x x x x Changes the text colors in this order:
title, @, underline, subtitle, colon, info
--underline on/off Enable/Disable the underline.
--underline_char char Character to use when underlining title
--bold on/off Enable/Disable bold text
COLOR BLOCKS:
--color_blocks on/off Enable/Disable the color blocks
--block_width num Width of color blocks in spaces
--block_height num Height of color blocks in lines
--block_range num num Range of colors to print as blocks
BARS:
--bar_char 'elapsed char' 'total char'
Characters to use when drawing bars.
--bar_border on/off Whether or not to surround the bar with '[]'
--bar_length num Length in spaces to make the bars.
--bar_colors num num Colors to make the bar.
Set in this order: elapsed, total
--cpu_display mode Bar mode.
Possible values: bar, infobar, barinfo, off
--memory_display mode Bar mode.
Possible values: bar, infobar, barinfo, off
--battery_display mode Bar mode.
Possible values: bar, infobar, barinfo, off
--disk_display mode Bar mode.
Possible values: bar, infobar, barinfo, off
IMAGE BACKEND:
--backend backend Which image backend to use.
Possible values: 'ascii', 'caca', 'jp2a', 'iterm2', 'off',
'sixel', 'tycat', 'w3m'
--source source Which image or ascii file to use.
Possible values: 'auto', 'ascii', 'wallpaper', '/path/to/img',
'/path/to/ascii', '/path/to/dir/'
--ascii source Shortcut to use 'ascii' backend.
--caca source Shortcut to use 'caca' backend.
--iterm2 source Shortcut to use 'iterm2' backend.
--jp2a source Shortcut to use 'jp2a' backend.
--kitty source Shortcut to use 'kitty' backend.
--pixterm source Shortcut to use 'pixterm' backend.
--sixel source Shortcut to use 'sixel' backend.
--termpix source Shortcut to use 'termpix' backend.
--tycat source Shortcut to use 'tycat' backend.
--w3m source Shortcut to use 'w3m' backend.
--off Shortcut to use 'off' backend (Disable ascii art).
NOTE: 'source; can be any of the following: 'auto', 'ascii', 'wallpaper', '/path/to/img',
'/path/to/ascii', '/path/to/dir/'
ASCII:
--ascii_colors x x x x x x Colors to print the ascii art
--ascii_distro distro Which Distro's ascii art to print
NOTE: Arch and Ubuntu have 'old' logo variants.
NOTE: Use 'arch_old' or 'ubuntu_old' to use the old logos.
NOTE: Ubuntu has flavor variants.
NOTE: Change this to 'Lubuntu', 'Xubuntu', 'Ubuntu-GNOME',
'Ubuntu-Studio' or 'Ubuntu-Budgie' to use the flavors.
NOTE: Alpine, Arch, CRUX, Debian, Gentoo, FreeBSD, Mac, NixOS,
OpenBSD, and Void have a smaller logo variant.
NOTE: Use '{distro name}_small' to use the small variants.
--ascii_bold on/off Whether or not to bold the ascii logo.
-L, --logo Hide the info text and only show the ascii logo.
IMAGE:
--loop Redraw the image constantly until Ctrl+C is used. This fixes issues
in some terminals emulators when using image mode.
--size 00px | --size 00% How to size the image.
Possible values: auto, 00px, 00%, none
--crop_mode mode Which crop mode to use
Takes the values: normal, fit, fill
--crop_offset value Change the crop offset for normal mode.
Possible values: northwest, north, northeast,
west, center, east, southwest, south, southeast
--xoffset px How close the image will be to the left edge of the
window. This only works with w3m.
--yoffset px How close the image will be to the top edge of the
window. This only works with w3m.
--bg_color color Background color to display behind transparent image.
This only works with w3m.
--gap num Gap between image and text.
NOTE: --gap can take a negative value which will move the text
closer to the left side.
--clean Delete cached files and thumbnails.
OTHER:
--config /path/to/config Specify a path to a custom config file
--config none Launch the script without a config file
--print_config Print the default config file to stdout.
--stdout Turn off all colors and disables any ASCII/image backend.
--help Print this text and exit
--version Show neofetch version
-v Display error messages.
-vv Display a verbose log for error reporting.
DEVELOPER:
--gen-man Generate a manpage for Neofetch in your PWD. (Requires GNU help2man)
Report bugs to https://github.com/dylanaraps/neofetch/issues

